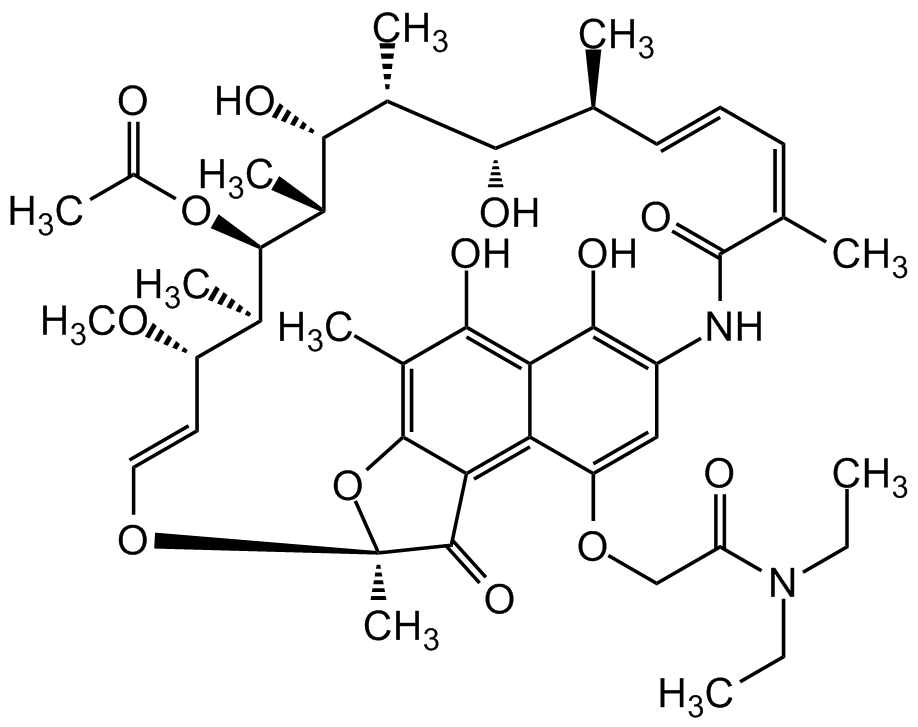
Rifamycin M14
Product Code:
AG-CN2-0332
AG-CN2-0332
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0332-M010 | 10 mg | £90.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0332-M050 | 50 mg | £330.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Rifamide; NCI 143-418; NSC 143418; RF M-14; Rifampicin M/14; N,N-Diethylamide-rifamycin B; Rifomycin B diethylamide
Appearance:
Yellow to orange powder.
CAS:
2750-76-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.Protect from light when in solution.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C43H58N2O13/c1-12-45(13-2)31(47)20-55-30-19-28-38(51)33-32(30)34-40(26(8)37(33)50)58-43(10,41(34)52)56-18-17-29(54-11)23(5)39(57-27(9)46)25(7)36(49)24(6)35(48)21(3)15-14-16-22(4)42(53)44-28/h14-19,21,23-25,29,35-36,39,48-51H,12-13,20H2,1-11H3,(H,44,53)/b15-14+,18-17+,22-16-/t21-,23+,24+,25+,29?,35-,36+,39+,43-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
VFYNXKZVOUXHDX-XXQVUONBSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 2750-76-7. Formula: C43H58N2O13. MW: 810.9. Semisynthetic. Ansamycin antibiotic. Selective inhibitor of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP). Effective against mycobacteria, and are therefore used in research of tuberculosis, leprosy and mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.
MDL:
MFCD00866814
Molecular Formula:
C43H58N2O13
Molecular Weight:
810.9
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Ansamycin antibiotic. Selective inhibitor of bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP). Effective against mycobacteria and therefore used in research of tuberculosis, leprosy and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections.
Purity:
>95% (HPLC)
SMILES:
OC1=C(NC(/C(C)=CC=C[C@H](C)[C@H](O)[C@@H](C)[C@H]([C@@H](C)[C@@H]([C@H](C)[C@H](/C=C/O2)OC)OC(C)=O)O)=O)C=C(OCC(N(CC)CC)=O)C3=C4C(O[C@@]2(C)C4=O)=C(C)C(O)=C31
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, aqueous acetonitrile or ethanol.
Source / Host:
Semisynthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
In vitro bacteriological studies on rifamycin B diethylamide (rifamide): R. Pallanza, et al.; Arzneimittelforschung 15, 800 (1965) | The inhibition of bacterial RNA synthesis by the rifamycin antibiotics: J.M. Wilhelm, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 166, 268 (1968) | Rifamycins: A General View: S. Riva & L.G. Silvestri; Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 26, 199 (1972) | Rifamycin antibiotics: inhibitors of Rauscher murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase and of purified DNA polymerases from human normal and leukemic lymphoblasts: S.S. Yang, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 49, 7 (1972) | Rifamycin Derivatives Strongly Inhibiting RNA>DNA Polymerase (Reverse Transcriptase) of Murine Sarcoma Viruses: C. Gurgo, et al.; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 49, 61 (1972) | Inhibition of poly(A) polymerase by rifamycin derivatives: S.T. Jacob & K.M. Rose; Nucl. Acids Res. 1, 1549 (1974) | Structure-Activity Relationships and DNA Polymerases From Normal and Specificity of Inhibition of Leukemia Cells of Man and From Simian Sarcoma Virus by Rifamycin Derivatives: R.A. CiCioccio & B.I.S. Srivastava; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 61, 1187 (1978) | Comparison of antibacterial and antiimmune effects of certain rifamycins: J.E. Kasik & M. Monick; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 19, 134 (1981) | In vitro activity of rifamycins alone and in combination with other antibiotics against Chlamydia trachomatis: R.B. Jones, et al.; Rev. Infect. Dis. 5, S556 (1983) | QSAR Modeling of Antimycobacterial Activity and Activity Against Other Bacteria of 3-Formyl Rifamycin SV Derivatives: D. Dimov, et al.; Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat. 20, 298 (2001)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Rifamycin AF | AG-CN2-0321 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rifamycin AF-API | AG-CN2-0325 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin AF-EPTAPI | AG-CN2-0326 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin AF-DA | AG-CN2-0328 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin AG | AG-CN2-0329 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin AMI-DA | AG-CN2-0330 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin AMP-DA | AG-CN2-0331 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin O | AG-CN2-0333 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin PR-14 | AG-CN2-0334 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin PR-3 | AG-CN2-0335 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rifamycin S, 8-Methyl- | AG-CN2-0337 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||