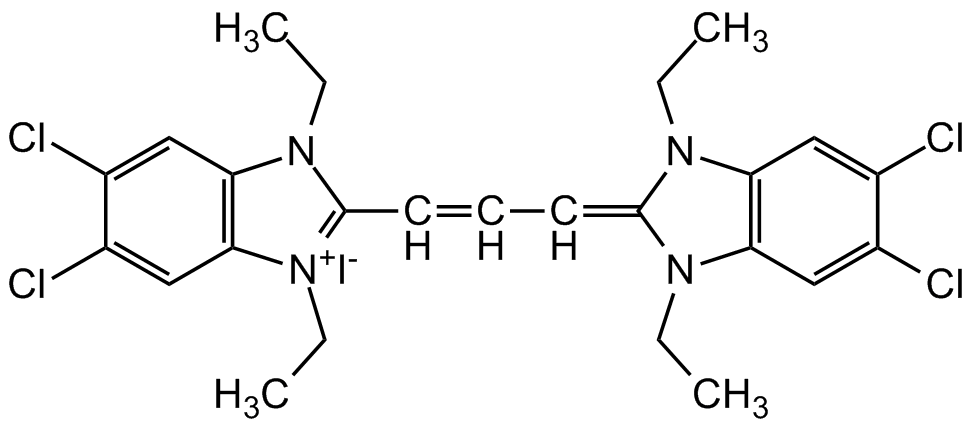
JC-1
Product Code:
AG-CR1-3568
AG-CR1-3568
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
-20°C
-20°C
Storage:
+4deg;C
+4deg;C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3568-M001 | 1 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3568-M005 | 5 mg | £175.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3568-5001 | 5 x 1 mg | £220.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5,5',6,6'-Tetrachloro-1,1',3,3'-tetraethylbenzimidazolylcarbocyanine iodide
Appearance:
Red powder.
CAS:
3520-43-2 and 47729-63-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C25H27Cl4N4.HI/c1-5-30-20-12-16(26)17(27)13-21(20)31(6-2)24(30)10-9-11-25-32(7-3)22-14-18(28)19(29)15-23(22)33(25)8-4;/h9-15H,5-8H2,1-4H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
InChiKey:
FYNNIUVBDKICAX-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 3520-43-2 and 47729-63-5. Formula: C25H27Cl4IN4. MW: 652.2. The membrane-permeant dual-emission potential-sensitive JC-1 dye is widely used in apoptosis studies to monitor mitochondrial health by flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy and in microplate-based fluorescent assays. JC-1 dye can be used as an indicator of mitochondrial membrane potential in a variety of cell types, including myocytes and neurons, as well as in intact tissues and isolated mitochondria. JC-1 accumulates in mitochondria, selectively generating an orange J-aggregate emission profile (590 nm) in healthy cells. After cell injury, as membrane potential decreases, JC-1 monomers are generated, resulting in a shift to green emission (529 nm). The principal advantage of JC-1 relative to other commonly employed fluorescent probes of mitochondrial membrane potential is that it allows qualitative visualization, considering the shift from orange to green fluorescence emission, and quantitative detection, considering the fluorescence intensity ratio.
MDL:
MFCD00188475
Molecular Formula:
C25H27Cl4IN4
Molecular Weight:
652.2
Other data:
Application Protocols: See literatures 8, 12 or 13 or the website protocol from Purdue University http://www.cyto.purdue.edu/archive/flowcyt/research/cytotech/apopto/data/cossar1/cossariz.htm .
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
The membrane-permeant dual-emission potential-sensitive JC-1 dye is widely used in apoptosis studies to monitor mitochondrial health by flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy and in microplate-based fluorescent assays. JC-1 dye can be used as an indicator of mitochondrial membrane potential in a variety of cell types, including myocytes and neurons, as well as in intact tissues and isolated mitochondria. JC-1 accumulates in mitochondria, selectively generating an orange J-aggregate emission profile (590 nm) in healthy cells. After cell injury, as membrane potential decreases, JC-1 monomers are generated, resulting in a shift to green emission (529 nm). The principal advantage of JC-1 relative to other commonly employed fluorescent probes of mitochondrial membrane potential is that it allows qualitative visualization, considering the shift from orange to green fluorescence emission, and quantitative detection, considering the fluorescence intensity ratio.
Purity:
>98% (NMR)
SMILES:
[I-].CCN1C(=CC=CC2=[N+](CC)C3=C(C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C3)N2CC)N(CC)C2=C1C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C2
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, methanol or acetone.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12171500
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
J-aggregate formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator of membrane potential: M. Reers, et al.; Biochemistry 30, 4480 (1991) | Intracellular heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane potentials revealed by a J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation JC-1: S.T. Smiley, et al.; PNAS 88, 3671 (1991) | A new method for the cytofluorimetric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using the J-aggregate forming lipophilic cation 5,5',6,6'-tetrachloro-1,1',3,3'-tetraethylbenzimidazolcarbocyanine iodide (JC-1): A. Cossarizza, et al.; BBRC 197, 40 (1993) | Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye: M. Reers, et al.; Methods Enzymol. 260, 406 (1995) | JC-1, but not DiOC6(3) or rhodamine 123, is a reliable fluorescent probe to assess delta psi changes in intact cells: implications for studies on mitochondrial functionality during apoptosis: S. Salvioli, et al.; FEBS Lett. 411, 77 (1997) | Functional assay of multidrug resistant cells using JC-1, a carbocyanine fluorescent probe: J.M. K?hnel, et al.; Leukemia 11, 1147 (1997) | Flow cytometric measurement of mitochondrial mass and function: a novel method for assessing chemoresistance: M. Mancini, et al.; Ann. Surg. Oncol. 5, 287 (1998) | Flow cytometric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using JC-1: A. Cossarizza & S. Salvioli; Curr. Protoc. Cytom. Chapter 9, Unit 9.14 (2001) (Protocol) | JC-1: a very sensitive fluorescent probe to test Pgp activity in adult acute myeloid leukemia: O. Legrand, et al.; Blood 97, 502 (2001) | Mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial reduction of MTT: interaction of MTT with TMRE, JC-1, and NAO mitochondrial fluorescent probes: T. Bernas & J. Dobrucki; Cytometry 47, 236 (2002) | JC-1, a sensitive probe for a simultaneous detection of P-glycoprotein activity and apoptosis in leukemic cells: D. Chaoui, et al.; Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 70, 189 (2006) | Polychromatic analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using JC-1: E. Lugli, et al.; Curr. Protoc. Cytom. Chapter 7, Unit 7.32 (2007) (Protocol) | Labeling mitochondria with JC-1: B. Chazotte; Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2011, (2011) (Protocol) | Stable Oxidative Cytosine Modifications Accumulate in Cardiac Mesenchymal Cells from Type2 Diabetes Patients: Rescue by Alpha-Ketoglutarate and TET-TDG Functional Reactivation: F. Spallotta, et al.; Circ. Res. Ahead of print (2017) | An alpha-synuclein decoy peptide prevents cytotoxic alpha-synuclein aggregation caused by fatty acid binding protein 3: N. Fukui, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 296, 100663 (2021)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | JC-10 (high purity) | AG-CR1-3600 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|