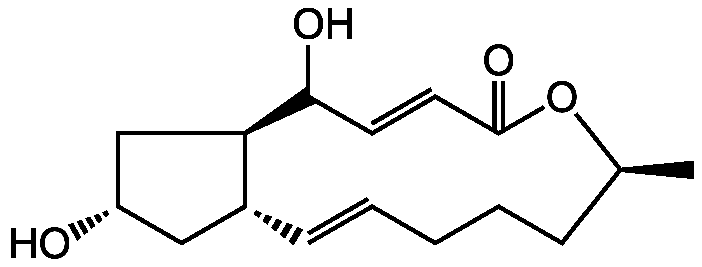
(+)-Brefeldin A
Product Code: AG-CN2-0018
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0018-M005 | 5 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0018-M010 | 10 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0018-M025 | 25 mg | £105.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20deg;C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
BFA; Ascotoxin; Decumbin; Cyanein; Synergisidin
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
20350-15-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Hazards:
H302, H312, H319, H332
InChi:
InChI=1S/C16H24O4/c1-11-5-3-2-4-6-12-9-13(17)10-14(12)15(18)7-8-16(19)20-11/h4,6-8,11-15,17-18H,2-3,5,9-10H2,1H3/b6-4+,8-7+/t11-,12+,13-,14+,15+/m0/s1
InChiKey:
KQNZDYYTLMIZCT-KQPMLPITSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 20350-15-6. Formula: C16H24O4. MW: 280.4. Isolated from Penicillium janthinellum. Protein transport from ER to Golgi inhibitor. ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) inhibitor. Cytotoxic. Antibiotic. Antiviral. Apoptosis inducer. Antitumor compound. Intracellular collagen degradation inhibitor. Reviews.
MDL:
MFCD12913297
Molecular Formula:
C16H24O4
Molecular Weight:
280.4
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P304, P340
Product Description:
Protein transport from ER to Golgi inhibitor [2, 3]. ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) inhibitor [6]. Cytotoxic [1]. Antibiotic [8]. Antiviral [8]. Apoptosis inducer [5]. Antitumor compound [9]. Intracellular collagen degradation inhibitor [7]. Reviews [4, 7, 8].
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
C[C@H]1CCCC=C[C@@H]2C[C@H](O)C[C@H]2C(O)C=CC(=O)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in acetone, DMSO, methanol or ethyl acetate (1mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Isolated from Penicillium janthinellum.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C.
References
Decumbin, a new compound from a species of Penicillium: V.L. Singleton, et al.; Nature 181, 1072 (1958) | Novel blockade by brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes: Y. Misumi, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 261, 11398 (1986) | Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum: T. Fujiwara, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 263, 18545 (1988) | Brefeldin A and the endocytic pathway. Possible implications for membrane traffic and sorting: W. Hunziker, et al.; FEBS Lett. 307, 93 (1992) (Review) | Brefeldin A is a potent inducer of apoptosis in human cancer cells independently of p53: R.G. Shao, et al.; Exp. Cell Res. 227, 190 (1996) | Inhibition by brefeldin A of a Golgi membrane enzyme that catalyses exchange of guanine nucleotide bound to ARF: J.B. Helms & J.E. Rothman; Nature 360, 352 (1992) | Brefeldin A: deciphering an enigmatic inhibitor of secretion: A. Nebenfuhr, et al.; Plant Physiol. 130, 1102 (2002) (Review) | Biological effects of the antibiotic brefeldin A (decumbin, cyanein, ascotoxin, synergisidin): a retrospective: V. Betina; Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 37, 3 (1992) (Review) | The cytotoxic agents NSC-95397, brefeldin A, bortezomib and sanguinarine induce apoptosis in neuroendocrine tumors in vitro: D.E. Larsson, et al.; Anticancer Res. 30, 149 (2010)