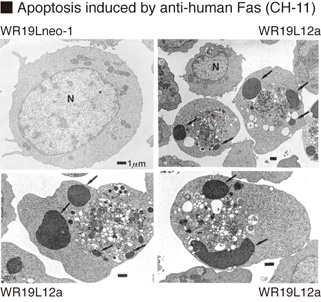
Antibody Clonality:
Monoclonal
Applications:- Flow Cytometry
- Western Blot (WB)
1 / 2
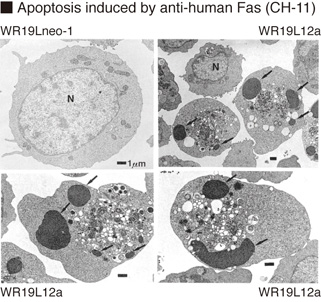
2 / 2
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available!
Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from:
United States.
Typical lead time:
10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
References
1) Yamaji, T., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 285, 35505-35518 (2010)
2) Arokium, H., et al., J. Virol. 83, 11283-11297 (2009)
3) Pallasch, C. P., et al., Blood 112, 4213-4219 (2008)
4) Conus, S., et al., J. Exp. Med. 205, 685-698 (2008)
5) Okamoto, K., et al., Genes Cells 11, 177-191 (2006)
6) Ohgushi, M., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 10017-10028 (2005)
7) Kotone-Miyahara, Y., et al., J. Leukoc. Biol. 76, 1047-1056 (2004)
8) Lee, K-K., et al., J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19276-19285 (2001)
9) Ichikawa, K., et al., Int. Immunol. 12, 555-562 (2000)
10) Tsukumo, S. I., et al., Genes Cells 4, 541-549 (1999)
11) Yamashita, K., et al., Blood 93, 674-685 (1999)
12) Ito, N., et al., Cell 66, 233-243 (1991)
13) Kobayashi, N., et al., PNAS 87, 9620-9624 (1990)
14) Yonehara, S., et al., J. Exp. Med. 169, 1747-1756 (1989)