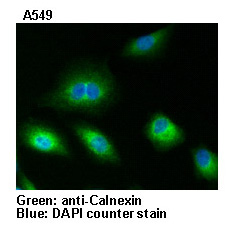
Anti-Calnexin pAb
Product Code:
MBL-PM060
MBL-PM060
Host Type:
Rabbit
Rabbit
Antibody Isotype:
Affinity Purified Ig
Affinity Purified Ig
Antibody Clonality:
Polyclonal
Polyclonal
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Human
Human
Applications:
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunoprecipitation (IP)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
4°C
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-PM060 | 100 ul | £334.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT