CircuLex Mouse/Rat PCSK9 ELISA Kit
Product Code:
MBL-CY-8078
MBL-CY-8078
Host Type:
Mixed
Mixed
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Application:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Shipping:
4°C
4°C
Storage:
4°C
4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-CY-8078 | 96 Assays | £551.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: United States.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Background:
PCSK9 (also known as neural apoptosis-regulated convertase, NARC-1) is a 692-residue extracellular protein expressed primarily in the kidneys, liver and intestines (1) representing the 9th member of the secretory subtilase family. Various genetic observations subsequently mapped PCSK9 as the third gene (along with LDLR and APOB) to cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia (ADH). These studies suggested that gain of function mutations increase plasma levels of LDL-c (2?6), whereas nonsense or missense (loss-of-function) mutations, which interfere with folding or secretion of PCSK9, lead to a reduction of plasma levels of LDL-c and an 88% decrease in the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) (5). In mice, adenoviral overexpression of PCSK9 results in increased plasma LDL-c level in normal mice but not in LDLR-deficient mice (7). Deletion of PCSK9 causes an increase in level of LDLR protein but not mRNA (8). These findings lead to a hypothesis that PCSK9 exerts its role in cholesterol metabolism through posttranslational down-regulation of LDLR, the receptor responsible for clearing LDL-c from plasma.
Evidence is consistent with the secreted form of PCSK9 binding directly to the LDLR and resulting in degradation of the receptor (9, 10). Zhang et al. (11) localized the binding site of PCSK9 in the LDLR to the first epidermal growth factor-like repeat (EGF-A) of the extracellular domain and showed that PCSK9 binding to this site is required for LDLR degradation. In light of these observations and the fact that PCSK9 in the circulation may cause the degradation of hepatic LDLR in the liver, PCSK9 would seem to be an attractive drug target for lowering LDL-c.
Description:
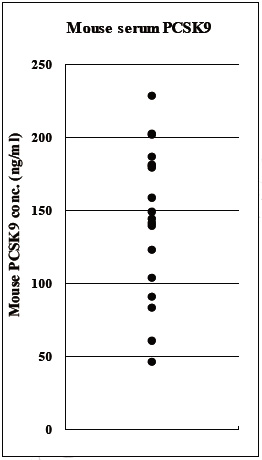
The CycLex Research Product CircuLex Mouse/Rat PCSK9 ELISA kit is used for the quantitative measurement of Mouse and Rat PCSK9 in serum, plasma, cell culture medium and other biological media.
Gene IDs:
Human: 255738 Mouse: 100102
Kit Components:
Microplate, Wash Buffer, Dilution Buffer, Mouse PCSK9 Standard, HRP conjugated Detection Antibody, Substrate Reagent, Stop Solution
Sensitivity:
better than 38.1 pg/ml of sample.
Target:
PCSK9
Documents
References
1. Seidah NG, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Marcinkiewicz J, Jasmin SB, Stifani S, Basak A, Prat A, Chretien M (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:928?933.
2. Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabes JP, Allard D, Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich D, et al. (2003) Nat Genet 34:154?156.
3. Leren TP (2004) Clin Genet 65:419?422.
4. Allard D, Amsellem S, Abifadel M, Trillard M, Devillers M, Luc G, Krempf M, Reznik Y, Girardet JP, Fredenrich A, et al. (2005) Hum Mutat 26:497.
5. Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH, Jr, Hobbs HH (2006) N Engl J Med 354, 1264?1272.
6. Berge KE, Ose L, Leren TP (2006) Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1094?1100.
7. Maxwell KN, Breslow JL (2004) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7100?7105.
8. Rashid S, Curtis DE, Garuti R, Anderson NN, Bashmakov Y, Ho YK, Hammer RE, Moon YA, Horton JD (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5374?5379.
9. Lagace, T. A., Curtis, D. E., Garuti, R., McNutt, M. C., Park, S. W., Prather, H. B., Anderson, N. N., Ho, Y. K., Hammer, R. E., and Horton, J. D. (2006) J. Clin. Investig. 116, 2995?3005
10. Cameron, J., Holla, O. L., Ranheim, T., Kulseth, M. A., Berge, K. E., and Leren, T. P. (2006) Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 1551?1558
11. Zhang, D. W., Lagace, T. A., Garuti, R., Zhao, Z., McDonald, M., Horton, J. D., Cohen, J. C., and Hobbs, H. H. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 18602?18612