Human IL-18 ELISA Kit
Product Code:
MBL-7620
MBL-7620
Host Type:
Human
Human
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Application:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Shipping:
4°C
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-7620 | 96 Wells | £603.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: United States.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternative Names:
interleukin 18 (interferon-γ-inducing factor)
Background:
Interleukin 18 (IL-18) is an 18 kDa cytokine which is identified as a costimulatory factor for production of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in response to toxic shock. It shares functional similarities with IL-12. IL-18 is synthesized as a precursor 24 kDa molecule without a signal peptide and must be cleaved to produce an active molecule. IL-1β converting enzyme (ICE, caspase-1) cleaves pro-IL-18 at aspartic acid in the P1 position, producing the mature, bioactive peptide that is readily released from the cells. It has been reported that IL-18 is produced from dendritic cells, activated macrophages, Kupffer cells, keratinocytes, intestinal epithelial cells, osteoblasts, adrenal cortex cells and murine diencephalons.
IFN-? is produced by activated T and NK cells and plays critical roles in the defense against microbial pathogens. IFN-γ activates macrophages, enhances NK activity and B cell maturation, proliferation and Ig secretion, induces MHC class I and II antigens expression, and inhibits osteoclast activation.
IL-18 acts on T helper 1-type (Th1) cells, and in combination with IL-12 strongly induces production of IFN-γ by these cells. Pleiotropic effects of IL-18 have also been reported, including enhancement production of IFN-γ and GM-CSF in peripheral blood mononuclear cells, production of Th1 cytokines, IL-2, GM-CSF and IFN-γ in T cells, enhancement of Fas ligand expression by Th1 cells.
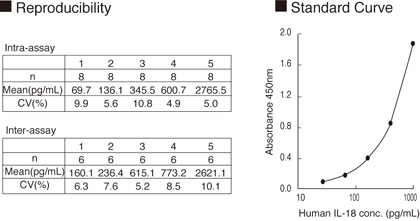
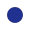
The ?Human IL-18 ELISA Kit? is a useful reagent for specifically measuring human IL-18 with high sensitivity by ELISA.
This Kit does not detect 1 ng/mL of various cytokines, such as human IFN-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-12, GM-CSF and murine IL-18. The results were all bellow the detection limit of 12.5 pg/mL.
Description:
The Human IL-18 ELISA kit measures human IL-18 by sandwich ELISA. The assay uses two
monoclonal antibodies against two different epitopes of human IL- 18. In the wells coated with
anti-human IL-18 monoclonal antibody, samples to be measured or standards are incubated. After
washing, a peroxidase-conjugated anti-human IL-18 monoclonal antibody is added into the
microwell and incubated. After another washing, the peroxidase substrate is mixed with the
chromogen and allowed to incubate for an additional period of time.
An acid solution is then added to each well to terminate the enzyme reaction and to
stabilize the developed color. The optical density (O.D.) of each well is measured at 450 nm using a
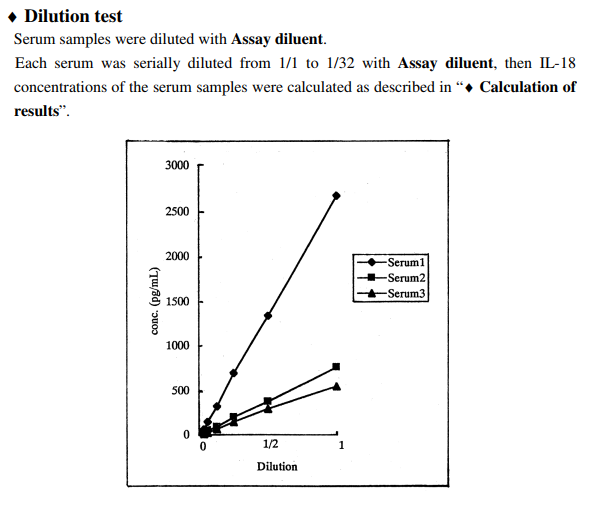
microplate reader. The concentration of human IL-18 is calibrated from a dose response curve based
on reference standards.
Gene IDs:
Human: 3606 Mouse: 16173
Kit Components:
Microwell strips coated with anti-Human IL-18 antibody 8-well strip x 12strips
Human IL-18 calibrator (Lyophilized) 2 vials
Conjugate reagent (Peroxidase conjugate anti-Human
IL-18 monoclonal antibody) ( x 101)
0.2mL x 1vial
Conjugate diluent (ready to use) 24mL x 1vial
Assay diluent (ready to use) 30mL x 1vial
Wash concentrate ( x 10) 100mL x 1vial
Substrate reagent (TMB/H2O2) (ready to use) 20mL x 1vial
Stop solution (2N H2SO4) (ready to use) (irritant) 18mL x ?vial
Target:
IL-18
Documents
References
1) Alsaleh, G., et al., J. Immunol. 182, 5088-5097 (2009)
2) Thompson, S. R., et al., Clin. Chemist. 53, 2078-2085 (2007)
3) Omoto, Y., et al., J. Immunol. 177, 8315-8319 (2006)
4) Vujisic, S., et al., Hum. Reprod. 21, 2650-2655 (2006)
5) Parikh, C. R., et al., J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 16, 3046-3052 (2005)
6) Tada, H., et al., Infect. Immunol. 73, 7967-7976 (2005)
7) Baratin, M. L., et al., PNAS. 102, 14747-14752 (2005)
8) Oku, H., et al., Hum. Reprod. 19, 709-714 (2004)
9) Kaizu, M., et al., Virology 313, 8-12 (2003)
10) Ahmad, R., et al., J. Virol. 76, 12448-12456 (2002)
11) Rouabhia, M., et al., Infect. Immunol. 75, 3739-3746 (2002)
12) Shida, K., et al., J. Immunol. 166, 6671-6679 (2001)
13) Narita, M., et al., Clin. Diagn. Lab. 7, 909-914 (2000)
14) Tao, D., et al., Cell Immunol. 173, 230-235 (1998)
15) Taniguchi, M., et al., J. Immunol. Methods 206, 107-113 (1997)
16) Micallef, M., et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 1647-1651 (1996)
17) Ushio, S., et al., J. Immunol. 156, 4274-4279 (1996)
18) Okamura, H., et al., Nature 378, 88-91 (1995)