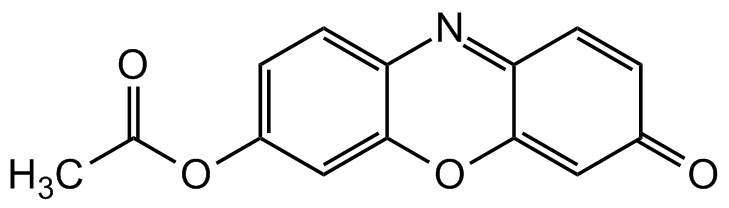
Resorufin acetate
Product Code:
CDX-R0020
CDX-R0020
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
AMBIENT
Storage:
Short term storage:+4°C. Long term storage:-20°C.
Short term storage:+4°C. Long term storage:-20°C.
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-R0020-M005 | 5 mg | £39.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-R0020-M025 | 25 mg | £126.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
O-acetyl Resorufin; 7-Acetyl-3H-phenoxazin-3-one
Appearance:
Orange to dark orange powder.
CAS:
1152-14-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302 + H332 - H315 - H319
InChi:
InChI=1S/C14H9NO4/c1-8(16)18-10-3-5-12-14(7-10)19-13-6-9(17)2-4-11(13)15-12/h2-7H,1H3
InChiKey:
UJWKHDKBOVPINX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 1152-14-3. Formula: C14H9NO4. MW: 255.23. Resorufin acetate is a fluorogenic substrate for hydrolytic esterases and cellulases used for monitoring cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH1A1) esterase activity, chymotrypsin activity. Resorufin acetate has been used as a novel indicator reaction for fluorometric detection of glucose using only glucose oxidase (GOD), without significant effects of ascorbic acid, uric acid, or bilirubin. It also has been used for the chromogenic and fluorescent detection of hydrazine, acyl protein thioesterase (APT) enzymes and perborate ions, and reveals a selective turn-on type chromogenic and fluorogenic signaling behavior based on the selective and efficient cleavage of acetate group. Upon enzymatic cleavage of the acetate group of resorufin acetate, the fluorescent hydrolysis product resorufin is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify enzyme activity. Spectral data of Resorufin: lambdaex=571nm, lambdaem=585nm.
MDL:
MFCD00037659
Molecular Formula:
C14H9NO4
Molecular Weight:
255.23
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261 - P264 - P301 + P312 - P302 + P352 - P304 + P340 + P312 - P305 + P351 + P338
Product Description:
Resorufin acetate is a fluorogenic substrate for hydrolytic esterases and cellulases used for monitoring cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH1A1) esterase activity, chymotrypsin activity. Resorufin acetate has been used as a novel indicator reaction for fluorometric detection of glucose using only glucose oxidase (GOD), without significant effects of ascorbic acid, uric acid, or bilirubin. It also has been used for the chromogenic and fluorescent detection of hydrazine, acyl protein thioesterase (APT) enzymes and perborate ions, and reveals a selective turn-on type chromogenic and fluorogenic signaling behavior based on the selective and efficient cleavage of acetate group. Upon enzymatic cleavage of the acetate group of resorufin acetate, the fluorescent hydrolysis product resorufin is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify enzyme activity. Spectral data of Resorufin: lambdaex=571nm, lambdaem=585nm.
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C1C=C2OC3=CC(OC(C)=O)=CC=C3N=C2C=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (5mg/ml) or DMF (20mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
(1) G.G. Guilbault & A.N.J. Heyn; Anal. Lett. 1, 163 (1967) | (2) T.M. Kitson & K.E. Kitson; Biochem J. 322, 701 (1997) | (3) T.M. Kitson & K.E. Kitson; Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 414, 201 (1997) | (4) T.M. Kitson; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1385, 43 (1998) | (5) H. Maeda, et al.; Chem. Pharm. Bull. 49, 294 (2001) | (6) M.G. Choi, et al.; Org. Lett. 12, 1468 (2010) | (7) M.G. Choi, et al.; Org. Biomol. Chem. 11, 2961 (2013)