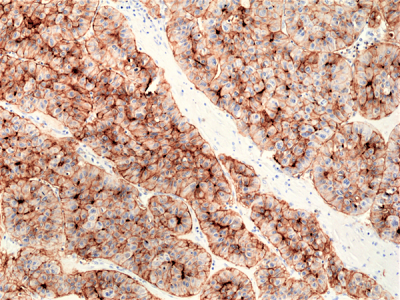
anti-CD73 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal (RM431)
Product Code:
REV-31-1319-00
REV-31-1319-00
Host Type:
Rabbit
Rabbit
Antibody Isotype:
Rabbit IgG
Rabbit IgG
Antibody Clonality:
Recombinant Antibody
Recombinant Antibody
Antibody Clone:
RM431
RM431
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Target Species:
Human
Human
Applications:
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Shipping:
BLUE ICE
BLUE ICE
Storage:
Long Term: -20°C
Long Term: -20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| REV-31-1319-00-R100 | 100 ul | £455.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 14-21 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 14-21 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5'-Nucleotidase; Ecto-5'-nucleotidase; 5'-NT; EC:3.1.3.5
Concentration:
N/A
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Formulation:
Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide.
Handling Advice:
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Immunogen:
A recombinant human CD73 protein.
Long Description:
Recombinant Antibody. This antibody RM431 reacts to human CD73. Application: IHC, WB . Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD73 (Ecto-5-prime-nucleotidase; 5-prime-ribonucleotide phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the conversion at neutral pH of purine 5-prime mononucleotides to nucleosides, the preferred substrate being AMP. CD73 is used as a marker of lymphocyte differentiation. Consequently, a deficiency of CD73 occurs in a variety of immunodeficiency diseases. CD73 is also a marker of undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells and is often used to identified stem cell populations. Defects in the CD73 gene can lead to the calcification of joints and arteries and intestinal tuberculosis. Extracellular adenosine is a potent endogenous immunosuppressive mediator critical to the maintenance of homeostasis in various normal tissues including the lung. Adenosine is either released from stressed or injured cells or generated from extracellular adenine nucleotides by the concerted action of the ectoenzymes ectoapyrase (CD39) and 5? ectonucleotidase (CD73) that catabolize ATP to adenosine. An acute CD73-dependent increase of adenosine in normal tissues mostly exerts tissue protective functions. CD73 is upregulated on a number of cancer cell types and catalyzes the conversion of extracellular nucleotides, such as AMP, to membrane-permeable nucleosides, such as adenosine; it plays a key role in adenosine-mediated immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment. High CD73 expression in the tumor tissue has been linked to poor overall survival and recurrence free survival in patients suffering from breast and ovarian cancer. CD73 and adenosine support growth-promoting neovascularization, metastasis and survival in cancer cells. In addition, adenosine can promote tumor intrinsic or therapy-induced immune escape by various mechanisms that dampen the immune system. Consequently, modulating CD73 or cancer-derived adenosine in the tumor microenvironment emerges as an attractive novel therapeutic strategy to limit tumor progression, improve antitumor immune responses, avoid therapy-induced immune deviation, and potentially limit normal tissue toxicity.
NCBI, Uniprot Number:
P21589
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
CD73 (Ecto-5-prime-nucleotidase; 5-prime-ribonucleotide phosphohydrolase) catalyzes the conversion at neutral pH of purine 5-prime mononucleotides to nucleosides, the preferred substrate being AMP. CD73 is used as a marker of lymphocyte differentiation. Consequently, a deficiency of CD73 occurs in a variety of immunodeficiency diseases. CD73 is also a marker of undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells and is often used to identified stem cell populations. Defects in the CD73 gene can lead to the calcification of joints and arteries and intestinal tuberculosis. Extracellular adenosine is a potent endogenous immunosuppressive mediator critical to the maintenance of homeostasis in various normal tissues including the lung. Adenosine is either released from stressed or injured cells or generated from extracellular adenine nucleotides by the concerted action of the ectoenzymes ectoapyrase (CD39) and 5? ectonucleotidase (CD73) that catabolize ATP to adenosine. An acute CD73-dependent increase of adenosine in normal tissues mostly exerts tissue protective functions. CD73 is upregulated on a number of cancer cell types and catalyzes the conversion of extracellular nucleotides, such as AMP, to membrane-permeable nucleosides, such as adenosine; it plays a key role in adenosine-mediated immunosuppression within the tumor microenvironment. High CD73 expression in the tumor tissue has been linked to poor overall survival and recurrence free survival in patients suffering from breast and ovarian cancer. CD73 and adenosine support growth-promoting neovascularization, metastasis and survival in cancer cells. In addition, adenosine can promote tumor intrinsic or therapy-induced immune escape by various mechanisms that dampen the immune system. Consequently, modulating CD73 or cancer-derived adenosine in the tumor microenvironment emerges as an attractive novel therapeutic strategy to limit tumor progression, improve antitumor immune responses, avoid therapy-induced immune deviation, and potentially limit normal tissue toxicity.
Purity:
Protein A purified.
Source / Host:
Rabbit
Specificity:
RM431 reacts to human CD73.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Primary Antibodies
UNSPSC Number:
12352203
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C.